How To Create Test Plan
This mind map focus on all the components that have primarily required while creating the test plans. 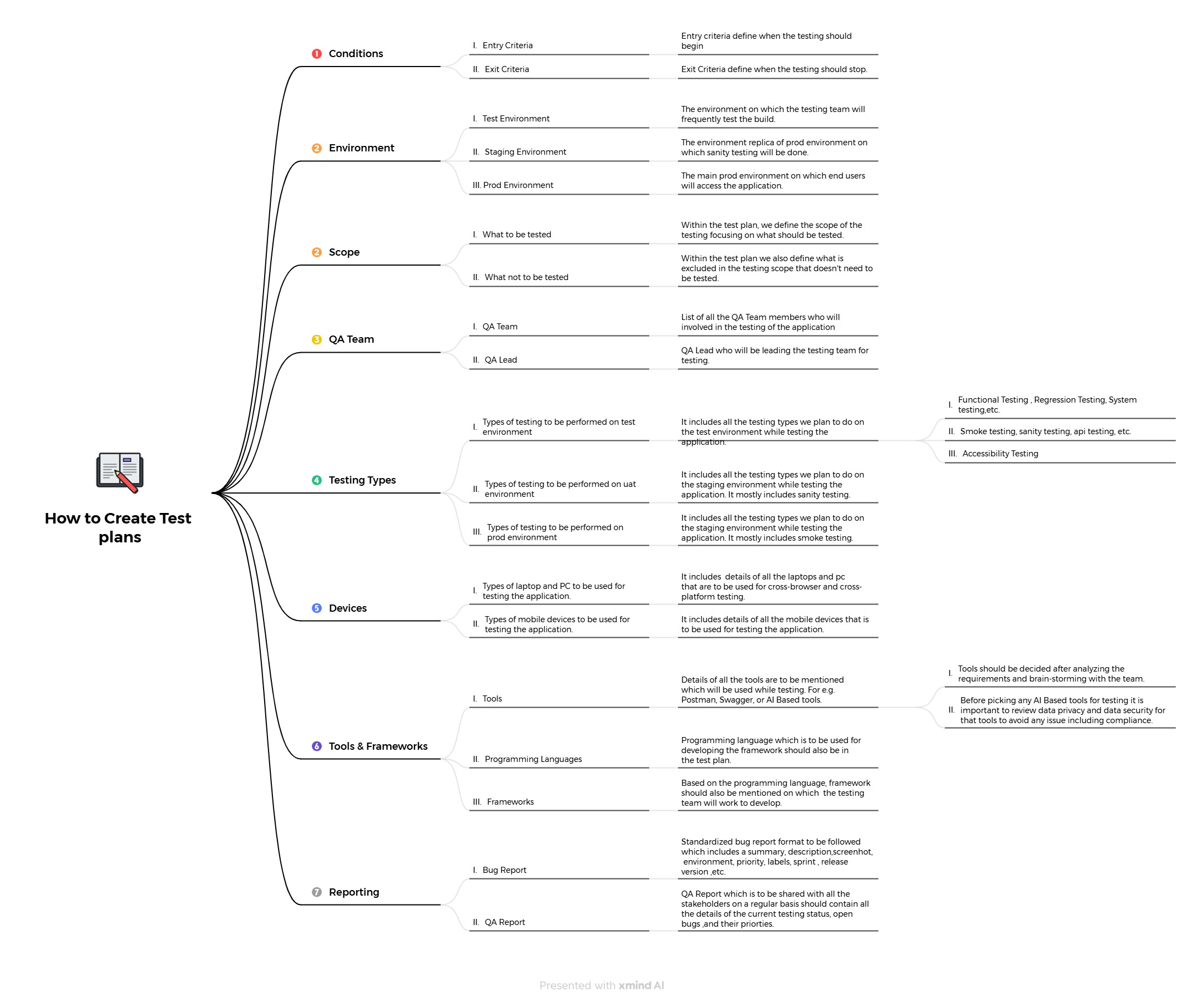
When creating a test plan, there are several essential components to consider for effective and thorough documentation, some of these components are :
1. Conditions: Test conditions define the entry and exit criteria that guide when testing should start and stop. Entry criteria ensure all prerequisites, such as environment setup, test data preparation, and build availability, are met before testing begins. Exit criteria specify the completion requirements, such as successful execution of test cases, defect resolution, and achieving predefined coverage metrics, to conclude the testing phase.
2. Environment: The test environment includes setups such as the testing, staging, and production environments. The test environment is frequently used for build validation, while the staging environment closely mirrors production for final checks. The production environment is the live system where end users access the application, and its settings must be replicated during pre-deployment testing for accuracy.
3. Scope: Defining the scope of the test plan is crucial for clarity on what is included or excluded. The scope outlines the features, modules, or functionalities to be tested, while also listing out-of-scope items to prevent ambiguity. This helps focus the testing efforts on priority areas and ensures alignment with project goals.
4. QA Team: The test plan must detail the team composition, including all QA team members involved in testing and their specific roles. The QA lead is responsible for overseeing the testing process, allocating tasks, and ensuring all testing objectives are met on schedule.
5. Testing Types: This section outlines the types of tests to be performed across various environments. The test environment typically includes functional, regression, and system testing. Smoke, sanity, and exploratory testing are common for the UAT environment, while accessibility and performance testing are often conducted in the production environment to ensure user readiness and compliance.
6. Devices: Test plans should list all hardware to be used, including laptops, PCs, and mobile devices. Details of laptops and PCs include configurations suitable for cross-browser and cross-platform testing, while mobile device specifications are crucial for testing compatibility across different screen sizes and operating systems.
7. Tools & Frameworks: The tools section identifies the testing tools and platforms, such as Postman for API testing or Selenium for automation, to be used during testing. It also includes programming languages and frameworks like Python or TestNG, which the QA team will use to develop and execute test cases. Before selecting any AI-based testing tools, considerations such as compliance with privacy and security standards are vital.
8. Reporting: Effective reporting is essential in a test plan, starting with standardized bug reports, which should include summaries, steps to reproduce, screenshots, and priority labels. QA reports provide a comprehensive overview of testing status, including open defects, resolved issues, and overall test progress, ensuring all stakeholders are updated and aligned.
